How To Read From Stdin Python
Take input from the user is an important part of any programming language. The output of the many programs depends on the standard input. The way of taking input from the user is different for unlike programming languages. Many means be in python to read from the standard input. The input() function is the most common way is to read from the standard input, which is a built-in function. The sys.stdin is another style is to read from the standard input the calls input() function internally. Python has another module named fileinput for reading the standard input. The input() office of this module can exist used to read standard input or read content from i or more files. Dissimilar ways to read from the standard input in Python take been explained in this tutorial.
Exampe-ane: Read data from stdin past using input() function
The input() function is the virtually used office to take input from the user. Create a python file with the post-obit script to take input from the user until the 'n' key is pressed. Here, an infinite loop is created by using the while loop. The first input() part is used to take the data from the user, and the print() function is used to print the input value. Next, the input() office of the script is used to enquire the user to keep the chore again or leave from the script. If the user presses 'n' or 'N', the loop'southward iteration will exist stopped by the pause statement; otherwise, the loop will iterate again and take another input from the user. The upper() role is used in the script to capitalize the value given by the user.
# Define an infinite loop
while True:
# Take input from the user
inputVal = input ( "Type whatever text:\n" )
# Impress the input value
impress ( "The input value is %south" %(inputVal) )
# Enquire for next iteration
nextInput = input ( "Do y'all want to keep? (Y/N)" )
# Terminate from the loop if 'n' is pressed
if nextInput.upper ( ) == 'N':
break
# Print the termination message
print ( "Program terminated." )
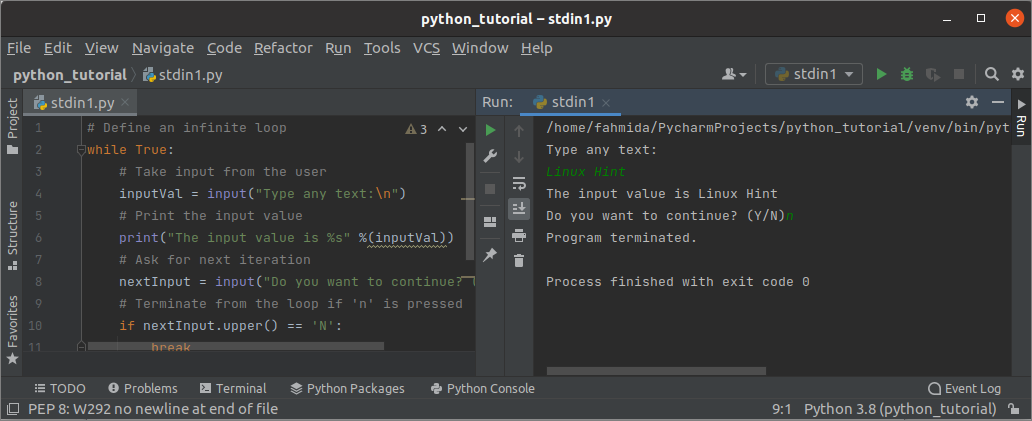
Output:
The post-obit similar output will appear subsequently executing the above script. Here, 'LinuxHint' has given as the first input value and terminated from the script for pressing the character, 'northward'.
Example-2: Read data from stdin past using sys.stdin
The sys.stdin is another option of Python to take standard input from the users from the terminal. It calls the input() function internally and adds '\north' after taking the input. Create a python file with the following script to check the use of the sys.stdin to take standard input. Here, the 'for-in' loop is used to have the input from the user infinite times until the user wants to terminate the script. After press the input value, the input() role is used to inquire the user to stop the script or not. The script will be terminated if the user presses 'y' or 'Y'. The upper() function is used here also to capitalize the input value.
# Import sys module
import sys
print ( "Type any text:" )
# Take input using stdin
for inputVal in sys.stdin:
# Print the input value
impress ( 'The input value is:%due south' % inputVal)
# Enquire for the next iteration
nextInput = input ( "Do you want to terminate? (Y/Northward)" )
# Cease from the loop if 'y/Y' is pressed
if nextInput.strip ( ).upper ( ) == 'Y':
break
else:
impress ( "Blazon any text:" )
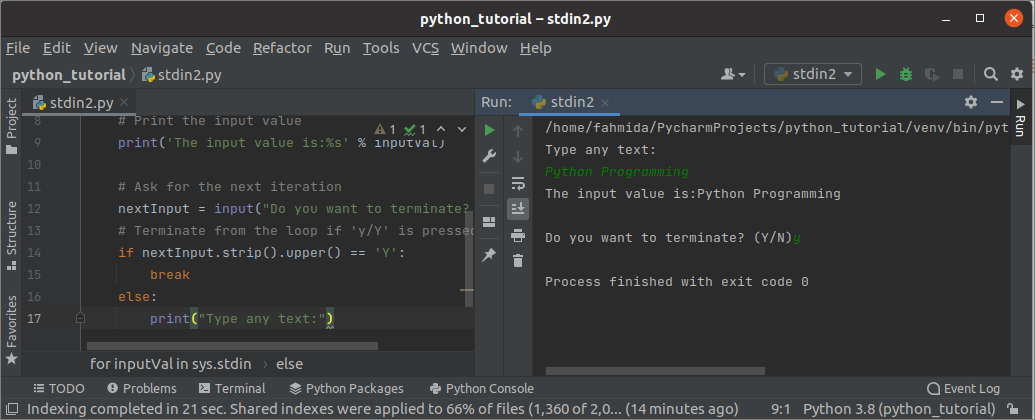
Output:
The following like output will appear afterward executing the above script. Hither, 'Python Programming' has given equally the first input value and terminated from the script for pressing the character, 'y'.
Example-three: Read information from stdin past using fileinput
The fileinput is some other module of Python to take standard input. The lines of text tin be taken from the terminal or a file by using fileinput.input(). If no argument value is provided in this part, it will take input from the terminal and if the name of an existing file is provided equally an argument value, it will take the input from the file. Create a python file with the following script to accept standard input from the terminal. Here, the 'for-in' loop is used as the previous case to take input for infinite times until the user wants to end the script. Next, the input() function is used to ask the user to stop the script or non. The script will exist terminated if the user types 'quit' or 'Quit' or 'QUIT'. The upper() role is used here too to capitalize the input value. The strip() function is used to remove the actress spaces from both sides of the input value.
# Import fileinput module
import fileinput
print ( "Enter the text:" )
''' Take input using fileinput.input() function and press ctrl+D to finish taking the input value '''
for inputVal in fileinput.input ( ):
# Terminate from the loop if 'quit' is typed
if inputVal.strip ( ).upper ( ) == "QUIT":
break
# Print the input value
print ( "The input value is:" , inputVal)
print ( "Enter the text:" )
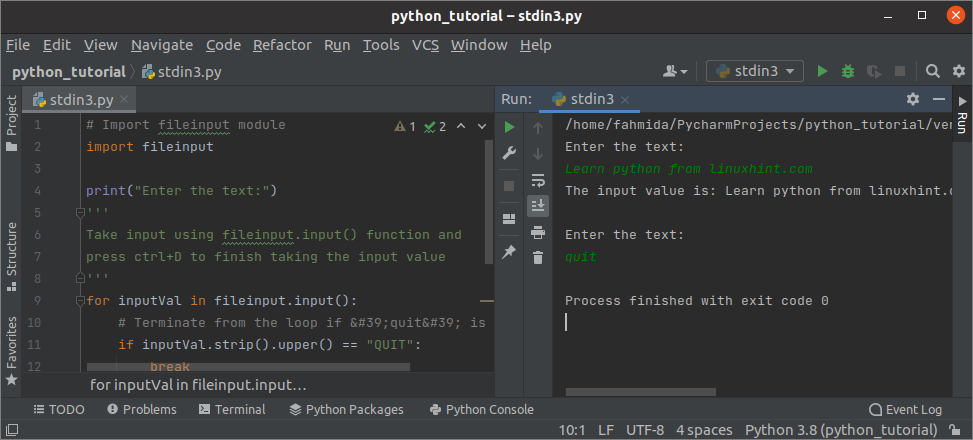
Output:
The following similar output volition appear after executing the higher up script. Hither, 'Acquire python from LinuxHint.com' has given as the kickoff input value and terminated from the script for typing the word, 'quit'. You take to recall i thing while taking input from the terminal using the fileinput module. That is, you have to printing ctrl+d after taking the input.
You accept to provide the filename as the argument value of the fileinput.input() office if you want to take data from the file instead of the final.
Decision:
Three different ways to accept input from the terminal take been shown in this tutorial by using three elementary examples. No module is required to employ the input() part for taking the input. The sys module is required to import for using sys.stdin, and the fileinput module is required to import for using fileinput.input() in the script to take standard input. I hope the Python users will take the standard input based on their requirements after reading this tutorial.
Source: https://linuxhint.com/read-from-stdin-in-python/

0 Response to "How To Read From Stdin Python"
Post a Comment